Lessons
Explore all newline lessons
lesson
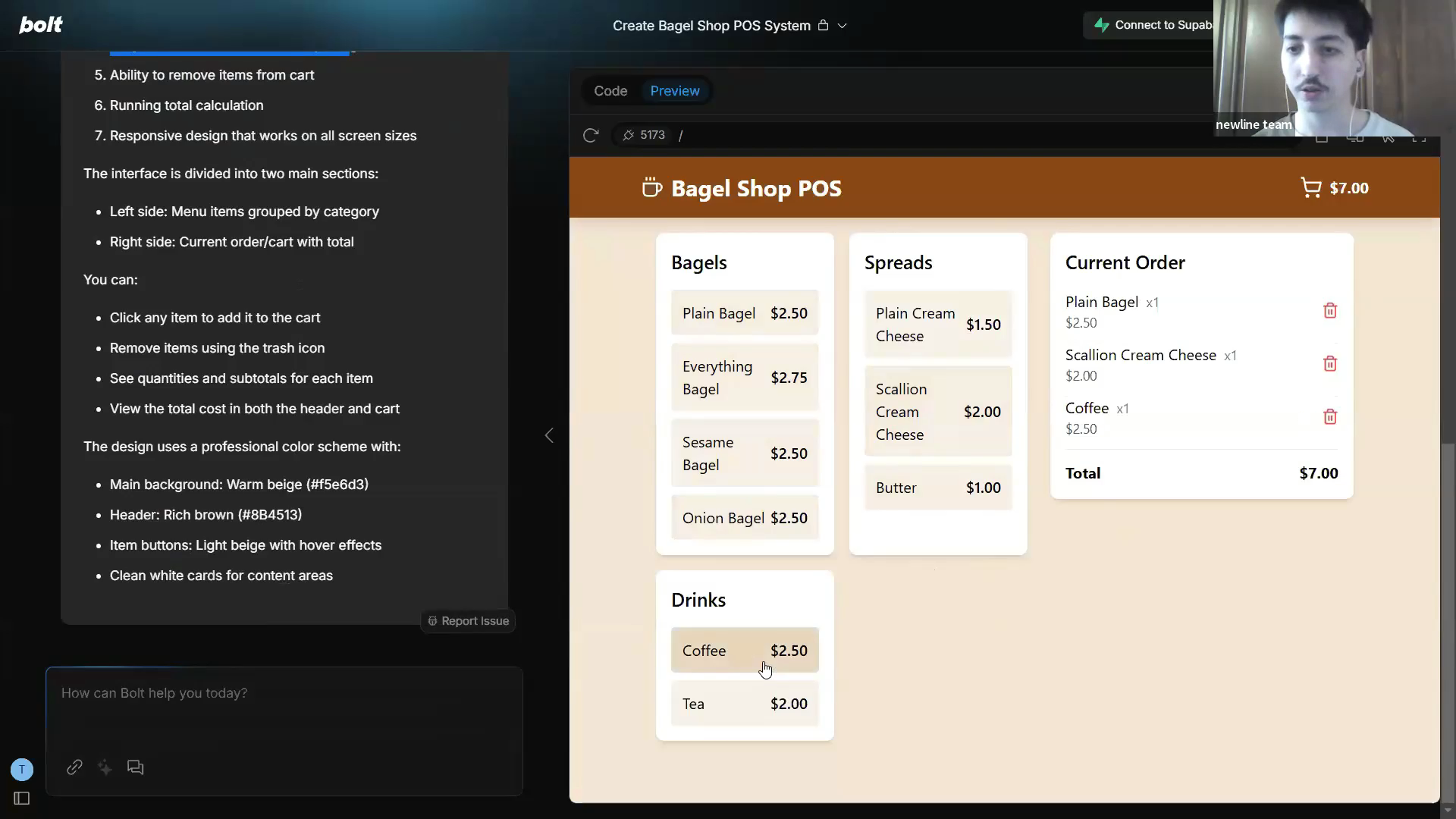
Advanced Prompt EngineeringPower AI course- Intro to Prompt Engineering and Why It Shapes Every LLM Response - How Prompts Steer the Probability Space of an LLM - Context Engineering for Landing in the Right “Galaxy” of Meaning - Normal Prompts vs Engineered Prompts and Why Specificity Wins - Components of a High-Quality Prompt: Instruction, Style, Output Format - Role-Based Prompting for Business, Coding, Marketing, and Analysis Tasks - Few-Shot Examples for Teaching Models How to Behave - Synthetic Data for Scaling Better Prompts and Personalization - Choosing the Right Model Using Model Cards and Targeted Testing - When to Prompt First vs When to Reach for RAG or Fine-Tuning - Zero-Shot, Few-Shot, and Chain-of-Thought Prompting Techniques - PAL and Code-Assisted Prompting for Higher Accuracy - Multi-Prompt Reasoning: Self-Consistency, Prompt Chaining, and Divide-and-Conquer - Tree-of-Thought and Branching Reasoning for Hard Problems - Tool-Assisted Prompting and External Function-Calling - DSPy for Automatic Prompt Optimization With Reward Functions - Understanding LLM Limitations: Hallucinations, Fragile Reasoning, Memory Gaps - Temperature, Randomness, and How to Control Output Stability - Defensive Prompting to Resist Prompt Injection and Attacks - Blocklists, Allowlists, and Instruction Defense for Safer Outputs - Sandwiching and Random Enclosure for Better Security - XML and Structured Tagging for Reliable, Parseable AI Output - Jailbreak Prompts and How Attackers Trick Models - Production-Grade Prompts for Consistency, Stability, and Deployment - LLM-as-Judge for Evaluating Prompt Quality and Safety - Cost Optimization: How Better Prompts Reduce Token Usage
lesson
Prompt Engineering- Intro to Prompt Engineering and Why It Shapes Every LLM Response - How Prompts Steer the Probability Space of an LLM - Context Engineering for Landing in the Right “Galaxy” of Meaning - Normal Prompts vs Engineered Prompts and Why Specificity Wins - Components of a High-Quality Prompt: Instruction, Style, Output Format - Role-Based Prompting for Business, Coding, Marketing, and Analysis Tasks - Few-Shot Examples for Teaching Models How to Behave - Synthetic Data for Scaling Better Prompts and Personalization - Choosing the Right Model Using Model Cards and Targeted Testing - When to Prompt First vs When to Reach for RAG or Fine-Tuning - Zero-Shot, Few-Shot, and Chain-of-Thought Prompting Techniques - PAL and Code-Assisted Prompting for Higher Accuracy - Multi-Prompt Reasoning: Self-Consistency, Prompt Chaining, and Divide-and-Conquer - Tree-of-Thought and Branching Reasoning for Hard Problems - Tool-Assisted Prompting and External Function-Calling - DSPy for Automatic Prompt Optimization With Reward Functions - Understanding LLM Limitations: Hallucinations, Fragile Reasoning, Memory Gaps - Temperature, Randomness, and How to Control Output Stability - Defensive Prompting to Resist Prompt Injection and Attacks - Blocklists, Allowlists, and Instruction Defense for Safer Outputs - Sandwiching and Random Enclosure for Better Security - XML and Structured Tagging for Reliable, Parseable AI Output - Jailbreak Prompts and How Attackers Trick Models - Production-Grade Prompts for Consistency, Stability, and Deployment - LLM-as-Judge for Evaluating Prompt Quality and Safety - Cost Optimization: How Better Prompts Reduce Token Usage